

Is 8-mm more effective than 4-mm-tip electrode catheter for ablation of typical atrial flutter? Circulation. Tsaï SF, Taï CT, Yu WC, Chen YJ, Hsieh MH, Chiang CE, et al. Tracking dynamic conduction recovery across the cavotricuspid isthmus. Shah DC, Takahashi A, Jaïs P, Hocini M, Peng JT, Clementy J, et al. P-wave morphology during right atrial pacing before and after atrial flutter ablation-a new marker for success. Hamdan MH, Kalman JM, Barron HV, Lesh MD. Double potentials along the ablation line as a guide to radiofrequency ablation of typical atrial flutter. Tada H, Oral H, Sticherling C, Chough SP, Baker RL, Wasmer K, et al. Differential pacing for distinguishing block from persistent conduction through an ablation line. Shah D, Haïssaguerre M, Takahashi A, Jaïs P, Hocini M, Clémenty J.
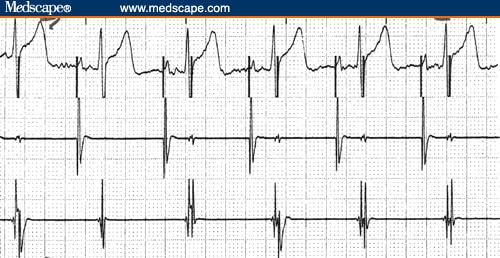
Long-term ECG monitoring using an implantable loop recorder for the detection of atrial fibrillation after cavotricuspid isthmus ablation in patients with atrial flutter. Mittal S, Pokushalov E, Romanov A, Ferrara M, Arshad A, Musat D, et al. Characteristics of cavotricuspid isthmus-dependent atrial flutter after left atrial ablation of atrial fibrillation. 2001 12:852–66.Ĭhugh A, Latchamsetty R, Oral H, Elmouchi D, Tschopp D, Reich S, et al. Classification of atrial flutter and regular atrial tachycardia according to electrophysiologic mechanism and anatomic bases: a statement from a joint expert group from the Working Group of Arrhythmias of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Saoudi N, Cosio F, Waldo A, Chen SA, Iesaka Y, Lesh M, et al. Effect of isthmus anatomy and ablation catheter on radiofrequency catheter ablation of the cavotricuspid isthmus. 1999 99:3017–23.ĭa Costa A, Faure E, Thévenin J, Messier M, Bernard S, Abdel K, et al. Angiographic anatomy of the inferior right atrial isthmus in patients with and without history of common atrial flutter. 2016 11:e0163383.Ĭabrera JA, Sanchez-Quintana D, Ho SY, Medina A, Wanguemert F, Gross E, et al. Clinical anatomy of the cavotricuspid isthmus and terminal crest. Klimek-Piotrowska W, Hołda MK, Koziej M, Hołda J, Piątek K, Tyrak K, et al. The architecture of the atrial musculature between the orifice of the inferior caval vein and the tricuspid valve: the anatomy of the isthmus. 1993 71:705–9.Ĭabrera JA, Sanchez-Quintana D, Ho SY, Medina A, Anderson RH. Radiofrequency ablation of the inferior vena cava–tricuspid valve isthmus in common atrial flutter. 1992 86:1233–40.Ĭosio FG, Lopez-Gil M, Giocolea A, Arribas F, Barroso JL. Radiofrequency catheter ablation for the treatment of human type I atrial flutter: identification of a critical zone in the reentrant circuit by endocardial mapping techniques. 1990 16:1639–48.įeld GK, Fleck P, Chen PS, Boyce K, Bahnson TD, Stein JB, et al. Demonstration of an area of slow conduction in human atrial flutter. Olshansky B, Okumura K, Hess PG, Waldo AL. This chapter focuses on the practical points for catheter ablation of CTI-dependent AFL. Radiofrequency (RF) catheter ablation of the CTI is considered a first-line therapy for treating CTI-dependent AFL. AFL is refractory to medical therapy and has now become routinely amenable to curative treatment by catheter ablation. Both clockwise (reverse typical or uncommon) and counterclockwise (typical or common) CTI-dependent AFL can occur, and counterclockwise AFL is the most commonly encountered in clinical practice presumably because the majority of triggers come from the left atrium (LA) and pulmonary veins (PVs). The triggers of AFL might be premature atrial contractions and/or atrial fibrillation (AF). These electrophysiologic characteristics enable sustainable macrooreentrant tachycardias around the tricuspid valve. The electrophysiologic substrate underlying AFL has been shown to be a combination of a slow conduction velocity in the CTI between the tricuspid annulus (TA) and inferior vena cava (IVC), and anatomic or functional conduction block along the crista terminalis and Eustachian ridge. Cavo-tricuspid isthmus (CTI)-dependent atrial flutter (AFL) is the most frequently encountered right atrial (RA) macroreentrant tachycardia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
